Explore the effective physical therapy techniques that alleviate symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), a common condition causing pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm. Physical therapy offers non-invasive approaches to relieve pressure on the median nerve, which runs through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. These techniques include exercises to strengthen muscles supporting the wrist and hand, stretches to improve flexibility, and manual therapy to reduce muscle tightness and improve joint mobility. By addressing underlying causes and promoting proper ergonomic practices, physical therapists help individuals manage CTS symptoms effectively. This blog delves into the top 10 physical therapy techniques tailored for carpal tunnel syndrome, providing insights into how these therapies can enhance mobility, alleviate pain, and improve overall hand function.
Best Physical therapy techniques for carpal tunnel syndrome
1. Nerve Gliding Exercises
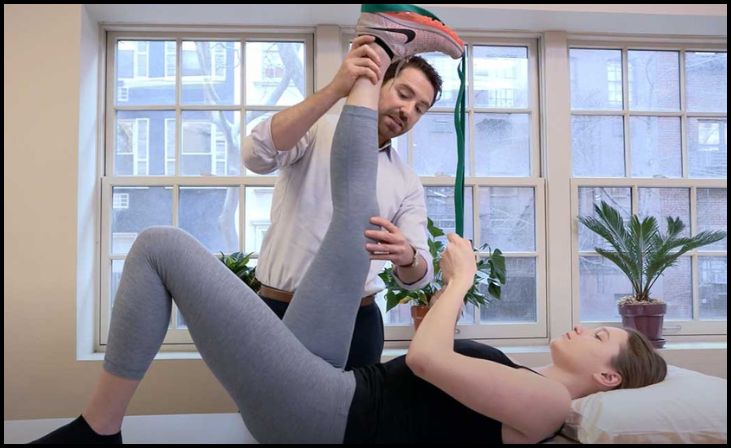

Nerve gliding exercises are a fundamental component of physical therapy for carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). These exercises aim to improve the mobility and flexibility of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. By gently stretching and mobilizing the nerve, physical therapists help reduce compression and alleviate symptoms such as numbness and tingling in the hand and fingers. Nerve gliding exercises are typically prescribed as part of a comprehensive treatment plan and may include movements that involve flexing, extending, and rotating the wrist and fingers to encourage smooth nerve function.
Read Also- 8 Best Physical Therapy for Scoliosis Management
2. Wrist Stretches
Wrist stretches are essential in relieving tightness and improving flexibility in the muscles and tendons surrounding the wrist joint. Physical therapists teach patients specific stretches targeting the wrist flexors, extensors, and rotators to reduce tension and pressure within the carpal tunnel. These stretches help maintain or restore normal range of motion in the wrist, which can alleviate symptoms of CTS such as pain and discomfort. Patients are encouraged to perform these stretches regularly throughout the day, especially during periods of repetitive wrist use or after prolonged periods of immobilization.
3. Splinting and Bracing
Splinting and bracing are commonly used techniques in physical therapy for CTS to immobilize the wrist in a neutral position, which helps reduce pressure on the median nerve. Splints are typically worn at night or during activities that exacerbate symptoms, such as typing or gripping tools. By keeping the wrist in a neutral or slightly extended position, splints prevent excessive flexion or compression of the carpal tunnel, allowing the median nerve to heal and reducing symptoms like numbness and tingling. Physical therapists assess the patient’s wrist alignment and recommend custom-fit splints or braces to provide optimal support and relief.
4. Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening exercises for the muscles of the hand, wrist, and forearm play a crucial role in stabilizing the wrist joint and improving overall function in individuals with CTS. Physical therapists prescribe specific exercises that target muscles such as the flexor and extensor muscles of the fingers and wrist, as well as the muscles that control thumb movement. Strengthening these muscles helps support the wrist joint, alleviate strain on the median nerve, and enhance grip strength and dexterity. Progressive resistance exercises using hand weights, resistance bands, or specialized equipment are tailored to each patient’s abilities and progression.
5. Ultrasound Therapy
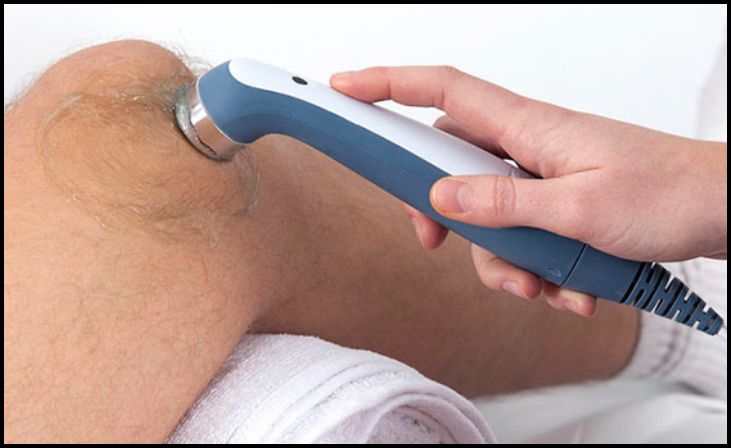
Ultrasound therapy is a therapeutic technique used in physical therapy for CTS to promote healing and reduce inflammation in the affected wrist tissues. High-frequency sound waves generated by an ultrasound machine penetrate deep into the tissues, producing a gentle heat that enhances blood flow and accelerates tissue repair. Ultrasound therapy is particularly beneficial for managing pain associated with CTS and can complement other therapeutic interventions such as exercises and manual therapy. Physical therapists carefully administer ultrasound therapy to target specific areas of the wrist affected by inflammation or swelling, helping patients achieve pain relief and improved functional outcomes.
6. Manual Therapy
Manual therapy techniques, including soft tissue mobilization, joint mobilization, and myofascial release, are effective in relieving muscle tension, improving joint mobility, and reducing pain in individuals with CTS. Physical therapists use their hands to apply controlled pressure and movements to the muscles, ligaments, and joints surrounding the wrist and hand. These techniques help release adhesions, improve tissue elasticity, and restore normal movement patterns. Manual therapy can also address secondary musculoskeletal issues that contribute to CTS symptoms, such as tightness in the forearm muscles or stiffness in the wrist joints. Sessions may be combined with other therapies to optimize therapeutic outcomes and promote long-term symptom relief.
7. Ergonomic Education
Ergonomic education is crucial in physical therapy for CTS to prevent aggravation of symptoms and promote healthy wrist habits. Physical therapists assess the patient’s workstation, daily activities, and ergonomic practices to identify potential risk factors contributing to CTS. They provide guidance on proper posture, wrist positioning, and workstation setup to minimize repetitive strain and pressure on the median nerve. Education on ergonomic principles empowers patients to make informed adjustments in their work and home environments, such as using ergonomic keyboards, adjusting chair height, and taking regular breaks from repetitive tasks. By promoting ergonomic awareness, physical therapists help patients manage CTS symptoms and maintain long-term wrist health.
8. Activity Modification
Activity modification involves adjusting daily activities and routines to reduce strain on the wrists and alleviate symptoms of CTS. Physical therapists work with patients to identify activities that exacerbate symptoms, such as prolonged typing, gripping tools, or repetitive wrist movements, and recommend modifications or alternatives. Strategies may include implementing rest breaks, alternating tasks between hands, using assistive devices, or practicing joint protection techniques. By modifying activities that contribute to wrist stress and overuse, individuals with CTS can better manage symptoms, prevent flare-ups, and promote healing of the median nerve.
9. Cold Therapy (Cryotherapy)
Cold therapy, or cryotherapy, is used in physical therapy for CTS to reduce pain and inflammation in the wrist. Therapists apply cold packs or ice wraps to the affected wrist area, which constricts blood vessels and decreases tissue swelling. Cold therapy helps numb nerve endings, providing temporary pain relief and reducing discomfort associated with CTS symptoms. This therapeutic technique is often used in conjunction with other treatments such as exercises or manual therapy to enhance overall effectiveness in managing pain and promoting recovery of wrist function.
10. Patient Education and Self-Management
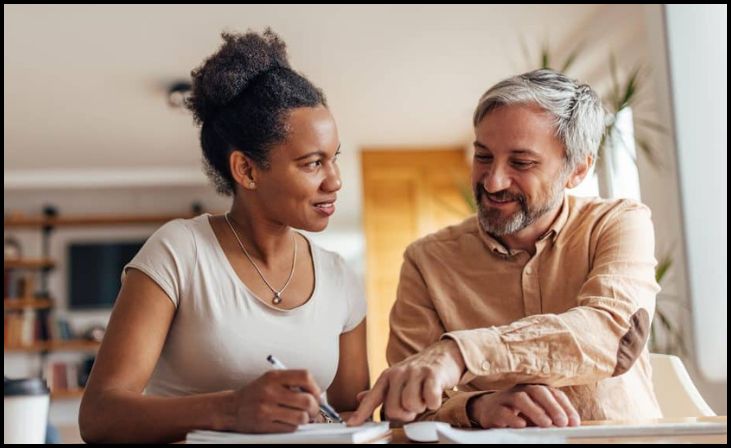

Patient education and self-management strategies are integral components of physical therapy for CTS, empowering individuals to take an active role in their treatment and recovery. Physical therapists educate patients about the anatomy of the wrist, the causes and symptoms of CTS, and the importance of adherence to treatment plans. They teach self-care techniques, including home exercises, ergonomic principles, and lifestyle modifications, to support ongoing symptom management and prevent recurrence. By fostering patient knowledge and self-efficacy, physical therapists promote long-term improvements in wrist function, pain relief, and overall quality of life for individuals living with CTS.
Conclusion
In conclusion, physical therapy offers effective strategies for managing carpal tunnel syndrome by addressing symptoms and improving wrist function. Through a combination of therapeutic techniques tailored to individual needs, physical therapists help alleviate pain, restore mobility, and prevent further nerve compression. Whether through specialized exercises, manual therapy, or ergonomic adjustments, physical therapy empowers individuals to regain control over their symptoms and enhance their quality of life. Take proactive steps towards managing carpal tunnel syndrome with the guidance of a skilled physical therapist to achieve lasting relief and improved hand and wrist health
FAQs
Which symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome are typical?
Thumb, index, and middle finger numbness or tingling, hand weakness, trouble holding items, and pain or discomfort that shoots up the arm are typical signs of carpal tunnel syndrome.
How may carpal tunnel syndrome be helped by physical therapy?
Physical therapy for carpal tunnel syndrome focuses on relieving pressure on the median nerve through techniques such as nerve gliding exercises, wrist stretches, and strengthening exercises for the muscles that support the wrist and hand.